Product Description
Our advantage:
*Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality
*Independent quality control department
*Control plan and process flow sheet for each batch
*Quality control in all whole production
*Meeting demands even for very small quantities or single units
*Short delivery times
*Online orders and production progress monitoring
*Excellent price-quality ratio
*Absolute confidentiality
*Various materials (stainless steel, iron, brass, aluminum, titanium, special steels, industrial plastics)
*Manufacturing of complex components of 1 – 1000mm.
Production machine:
| Specification | Material | Hardness |
| Z13 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z16 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z18 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z20 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z26 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z28 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Custom dimensions according to drawings | Steel | HRC35-40 |
Production machine:
Inspection equipment :
Gear tester
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

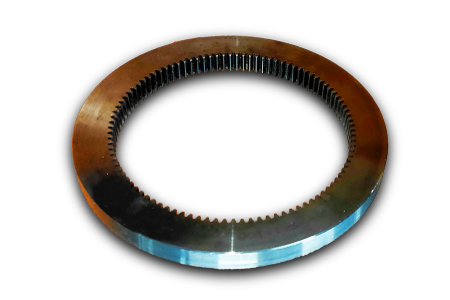
How do ring gears contribute to power transmission?
Ring gears play a significant role in power transmission within mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how ring gears contribute to power transmission:
- Torque Transfer: Ring gears are designed with teeth on their outer or inner circumference, depending on whether they are external or internal ring gears. These teeth mesh with the teeth of other gears, such as pinion gears or planetary gears. As the driving gear rotates, the meshing teeth engage with the ring gear’s teeth, transmitting torque from the driving gear to the ring gear. This torque transfer enables the ring gear to rotate and transmit power to other components or systems connected to it.
- Rotational Motion: Ring gears convert the rotational motion of the driving gear into rotational motion of the ring gear itself. The teeth on the ring gear provide a positive engagement with the teeth of the driving gear, ensuring a synchronized rotation. As the driving gear rotates, the meshing teeth push against the ring gear’s teeth, causing it to rotate in the same direction and at a proportional speed determined by the gear ratio. This rotational motion is crucial for transmitting power to different parts of the system or driving various mechanisms and components.
- Speed Reduction or Increase: Ring gears, in conjunction with other gears in the system, can be used to achieve speed reduction or increase. By varying the sizes of the driving gear, the ring gear, and other intermediate gears, different gear ratios can be achieved. When the driving gear is smaller than the ring gear, the ring gear rotates at a slower speed than the driving gear, resulting in speed reduction. Conversely, if the driving gear is larger, the ring gear rotates at a faster speed, leading to speed increase. This ability to control gear ratios allows for power transmission at desired speeds and enables systems to meet specific operational requirements.
- Load Distribution: Ring gears distribute the transmitted loads across their circumference. The teeth of the ring gear engage with multiple teeth of other gears, ensuring that the load is shared among these meshing points. This load distribution helps prevent localized stress concentrations and excessive wear on specific gear teeth. By distributing the load, ring gears contribute to the overall durability and longevity of the gear system, allowing for reliable power transmission even under demanding conditions.
- Compact and Efficient Design: Ring gears offer a compact and efficient design for power transmission. Their annular shape allows for a high gear ratio within a small space, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. Additionally, ring gears can be integrated into various gear configurations, such as planetary gear systems or gearboxes, which further enhance their power transmission capabilities. This compact and efficient design contributes to overall system efficiency and performance.
Overall, ring gears are essential components in power transmission systems. Through torque transfer, rotational motion, speed control, load distribution, and their compact design, ring gears enable efficient and reliable power transmission in a wide range of mechanical applications.
How do you maintain and service a ring gear system?
Maintaining and servicing a ring gear system is crucial to ensure its optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance and service procedures for a ring gear system:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the ring gear system to detect any signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or abnormal conditions. Inspect the gear teeth for chips, cracks, or excessive wear. Check for proper gear engagement and backlash. Inspect the mounting bolts or fasteners for tightness. Regular inspections help identify potential issues early on and prevent further damage or failures.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Clean the ring gear system periodically to remove dirt, debris, and old lubricant. Use appropriate cleaning methods and solvents that are compatible with the gear system materials. After cleaning, apply fresh lubricant according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Ensure proper lubrication coverage and distribution to minimize friction, wear, and heat generation.
- Lubricant Analysis: Periodically analyze the condition of the lubricant in the ring gear system to assess its effectiveness and detect any contamination or degradation. Lubricant analysis involves collecting samples and sending them to a laboratory for testing. The analysis results can provide valuable information about the lubricant’s viscosity, contamination levels, and overall condition. Based on the analysis, determine whether lubricant replacement or additional maintenance actions are necessary.
- Bearing and Seal Inspection: If the ring gear system includes bearings or seals, inspect them regularly for wear, damage, or leaks. Check for excessive play, noise, or overheating in the bearings. Inspect the seals for proper sealing and lubricant retention. Replace any worn-out bearings or damaged seals to prevent further damage to the ring gear system.
- Torque Checks: Periodically check the torque of the mounting bolts or fasteners that secure the ring gear system. Over time, vibrations and operational stresses can cause bolts to loosen. Ensure that the bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Perform torque checks during scheduled maintenance intervals or when any signs of loosening are observed.
- Alignment and Gear Meshing: Check and adjust the alignment of the ring gear system if necessary. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, increased load on the gear teeth, and reduced performance. Ensure proper gear meshing and backlash according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Adjust the gear positioning or contact pattern if deemed necessary during inspections or maintenance activities.
- Repair or Replacement: If any significant damage, wear, or malfunction is identified during inspections or maintenance activities, plan for repair or replacement of the affected components. Depending on the severity and nature of the issue, repairs may involve repairing gear teeth, replacing damaged parts, or realigning the gear system. If extensive damage is present or the gear system has reached the end of its service life, consider replacing the entire ring gear system.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed documentation and records of all maintenance and service activities performed on the ring gear system. Keep track of inspection results, lubrication schedules, repairs, parts replacements, and any other relevant information. These records help establish a maintenance history, track performance trends, and provide valuable reference information for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
It’s important to note that the specific maintenance and service procedures may vary depending on the type of ring gear system, its application, and the manufacturer’s guidelines. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and consult with experts or professionals when necessary to ensure proper maintenance and servicing of the ring gear system.
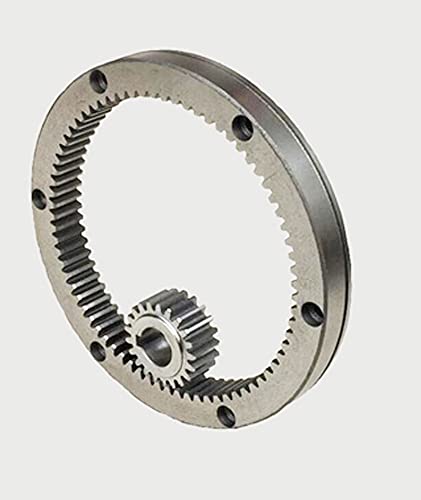

How do ring gears differ from other types of gears?
Ring gears, also known as annular gears or internal gears, possess distinct characteristics that set them apart from other types of gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of how ring gears differ from other gears:
1. Tooth Configuration: The most significant difference between ring gears and other gears is their tooth configuration. In a ring gear, the teeth are located on the inside circumference of a circular ring, whereas in other gears such as spur gears, helical gears, and bevel gears, the teeth are present on the outer surface of the gear. This internal tooth arrangement makes ring gears unique and allows them to mesh with pinion gears or other external gears.
2. Gear Assembly: The assembly of ring gears differs from other gears. In most cases, ring gears are used in combination with pinion gears or other external gears. The pinion gear meshes with the teeth on the inside of the ring gear. This gear set configuration enables the transmission of rotational motion and torque.
3. Load Distribution: Ring gears distribute the load over a larger area compared to other types of gears. The load is spread across the internal teeth of the ring gear, resulting in improved load-carrying capacity and enhanced gear durability. This load distribution characteristic makes ring gears suitable for applications that involve high loads or continuous operation.
4. Gear Ratio: Ring gears offer specific advantages in terms of gear ratios. They are commonly used in applications where high gear ratios are required. The gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the ring gear compared to the number of teeth on the mating gear (such as a pinion gear). The internal tooth configuration of the ring gear allows for larger gear diameters, enabling higher gear ratios to be achieved.
5. Space Utilization: Ring gears provide a compact design compared to some other types of gears. The internal tooth arrangement allows for a more space-efficient gear assembly. This compactness is advantageous in applications where space is limited or where a high gear ratio needs to be achieved within a confined area.
6. Applications: Ring gears are commonly used in automotive transmissions, differential systems, planetary gear systems, industrial machinery, robotics, power generation equipment, and heavy machinery. Their unique characteristics make them suitable for applications that require precise motion control, load distribution, and high gear ratios.
It’s important to note that the specific design, tooth profile, material selection, and manufacturing techniques may vary for different types of gears, including ring gears. Each type of gear is designed to meet specific application requirements, operating conditions, and performance needs.


editor by CX 2024-04-15