Product Description
Product Description
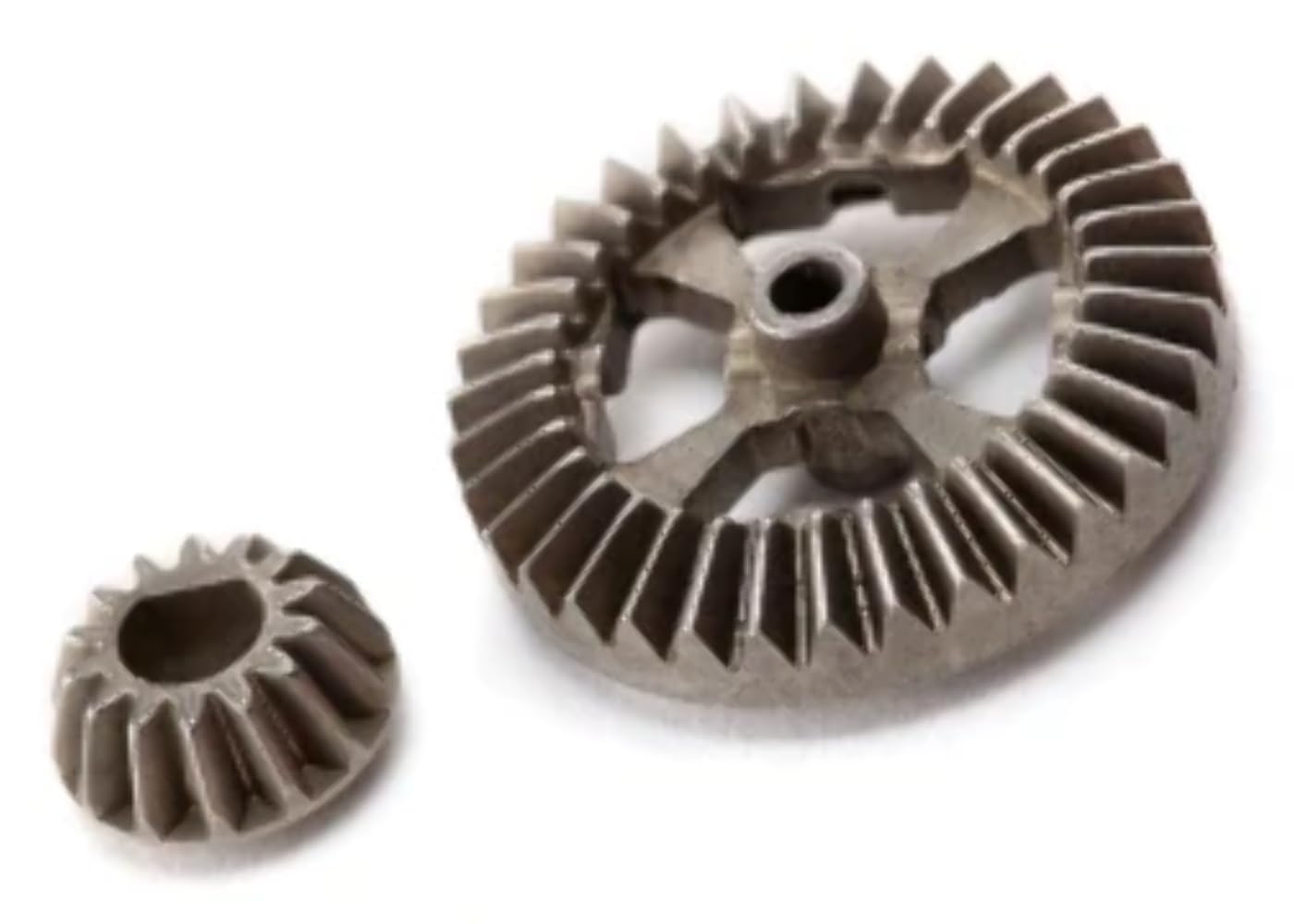
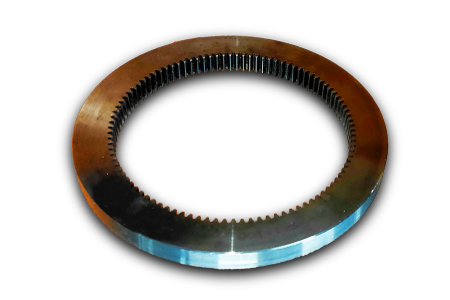
A herringbone gear is a specific type of double helical gear. Each helical groove of this gear looks like the letter V, and many together form a herringbone pattern.
Kingrail Parts can produce all kinds of herringbone gear for mining machinery, mills, kilns and other equipment.
Specifications:
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
Herringbone gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
Forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
Hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
Up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
Kingrail Parts can customize herringbone gear according to customer’s specifications and requirements
Manufacturing process:
Rraw matrial — Forging testing– Turning — Drilling — Heat Treatment — Milling– Grinding — Shaping and hobbing Process — Packing — Shipping
After Sales Service
1. OEM and customized service.
2. Full machining, primer coating, surface treatment.
3. Complete material testing process.
4. Quality control
Contact us
If you have any questions, pls feel free to contact us
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What lubrication is required for ring gears?
Proper lubrication is essential for the optimal performance and longevity of ring gears. Here’s a detailed explanation of the lubrication requirements for ring gears:
- Type of Lubricant: The type of lubricant used for ring gears depends on various factors, including the application, operating conditions, and gear design. Common lubricants for ring gears include gear oils, grease, and synthetic lubricants. Gear oils are specifically formulated for gear systems and provide excellent lubrication and protection against wear. Grease is often used in applications where the gear system operates at lower speeds or requires higher viscosity lubrication. Synthetic lubricants offer enhanced performance, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures and loads.
- Lubricant Properties: The lubricant chosen for ring gears should possess certain properties to ensure effective lubrication. These properties include high film strength, good thermal stability, resistance to oxidation, and anti-wear characteristics. The lubricant should also be compatible with the materials used in the ring gear system to prevent damage or degradation of the gear surfaces.
- Viscosity: Viscosity is an important consideration when selecting lubrication for ring gears. Viscosity refers to the thickness or resistance to flow of the lubricant. It is crucial to choose a lubricant with the appropriate viscosity to ensure proper lubrication film formation between the gear teeth. If the lubricant’s viscosity is too low, it may not provide sufficient lubrication, leading to increased wear. Conversely, if the viscosity is too high, it may cause excessive friction and energy loss. The recommended viscosity range is typically specified by the gear manufacturer or industry standards.
- Lubrication Method: The lubrication method for ring gears can vary depending on the specific application and gear system design. For enclosed gear systems, such as gearboxes or sealed housings, lubrication is typically performed by filling the housing with the recommended lubricant to the appropriate level. In open gear systems, such as large industrial gears, lubricant application methods may include spray systems, drip lubrication, or circulation systems. The lubrication method should ensure sufficient coverage and distribution of the lubricant to all gear surfaces.
- Lubrication Frequency: Regular lubrication maintenance is crucial to keep ring gears properly lubricated. The frequency of lubrication depends on the operating conditions, gear system design, and the lubricant used. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations or industry standards regarding lubrication intervals. Regular inspections should also be conducted to monitor the lubricant condition, check for contamination, and replenish or replace the lubricant as needed.
- Environmental Considerations: Environmental factors, such as temperature, moisture, and contamination, can affect the performance of the lubricant and the ring gears. It is important to consider these factors when selecting the lubricant. Extreme temperatures may require lubricants with enhanced thermal stability, while exposure to moisture or harsh contaminants may necessitate lubricants with better resistance to corrosion or water washout.
To ensure the proper lubrication of ring gears, it is advisable to consult the gear manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines. They can provide specific information regarding the suitable lubricant type, viscosity range, lubrication method, and maintenance practices for the particular ring gear system.
How do you maintain and service a ring gear system?
Maintaining and servicing a ring gear system is crucial to ensure its optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance and service procedures for a ring gear system:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the ring gear system to detect any signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or abnormal conditions. Inspect the gear teeth for chips, cracks, or excessive wear. Check for proper gear engagement and backlash. Inspect the mounting bolts or fasteners for tightness. Regular inspections help identify potential issues early on and prevent further damage or failures.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Clean the ring gear system periodically to remove dirt, debris, and old lubricant. Use appropriate cleaning methods and solvents that are compatible with the gear system materials. After cleaning, apply fresh lubricant according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Ensure proper lubrication coverage and distribution to minimize friction, wear, and heat generation.
- Lubricant Analysis: Periodically analyze the condition of the lubricant in the ring gear system to assess its effectiveness and detect any contamination or degradation. Lubricant analysis involves collecting samples and sending them to a laboratory for testing. The analysis results can provide valuable information about the lubricant’s viscosity, contamination levels, and overall condition. Based on the analysis, determine whether lubricant replacement or additional maintenance actions are necessary.
- Bearing and Seal Inspection: If the ring gear system includes bearings or seals, inspect them regularly for wear, damage, or leaks. Check for excessive play, noise, or overheating in the bearings. Inspect the seals for proper sealing and lubricant retention. Replace any worn-out bearings or damaged seals to prevent further damage to the ring gear system.
- Torque Checks: Periodically check the torque of the mounting bolts or fasteners that secure the ring gear system. Over time, vibrations and operational stresses can cause bolts to loosen. Ensure that the bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Perform torque checks during scheduled maintenance intervals or when any signs of loosening are observed.
- Alignment and Gear Meshing: Check and adjust the alignment of the ring gear system if necessary. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, increased load on the gear teeth, and reduced performance. Ensure proper gear meshing and backlash according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Adjust the gear positioning or contact pattern if deemed necessary during inspections or maintenance activities.
- Repair or Replacement: If any significant damage, wear, or malfunction is identified during inspections or maintenance activities, plan for repair or replacement of the affected components. Depending on the severity and nature of the issue, repairs may involve repairing gear teeth, replacing damaged parts, or realigning the gear system. If extensive damage is present or the gear system has reached the end of its service life, consider replacing the entire ring gear system.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed documentation and records of all maintenance and service activities performed on the ring gear system. Keep track of inspection results, lubrication schedules, repairs, parts replacements, and any other relevant information. These records help establish a maintenance history, track performance trends, and provide valuable reference information for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
It’s important to note that the specific maintenance and service procedures may vary depending on the type of ring gear system, its application, and the manufacturer’s guidelines. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and consult with experts or professionals when necessary to ensure proper maintenance and servicing of the ring gear system.

What is a ring gear and how does it work?
A ring gear is a type of gear that features teeth on the outer perimeter of a circular ring-shaped component. It is commonly used in various mechanical systems and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a ring gear is and how it works:
A ring gear, also known as an annular gear or internal gear, is a gear with teeth on the inside circumference of a circular ring. It is designed to mesh with a pinion gear or another gear that has teeth on the outside. The combination of a ring gear and a pinion gear forms a gear set, enabling the transmission of rotational motion and torque between the two gears.
Here’s how a ring gear works:
- Tooth Engagement: When a ring gear and a pinion gear are brought together, the teeth of the pinion gear mesh with the teeth of the ring gear. The teeth of the pinion gear enter the spaces between the teeth of the ring gear, creating a mechanical connection between the two gears.
- Motion Transmission: As the driving gear (such as the pinion gear) rotates, it transfers rotational motion to the ring gear. The teeth of the driving gear push against the teeth of the ring gear, causing the ring gear to rotate in the opposite direction. This rotational motion can be used to drive other components or systems connected to the ring gear.
- Torque Transfer: The meshing of the teeth between the ring gear and the driving gear allows for the transfer of torque. Torque is the rotational force or twisting force applied to a gear. As the driving gear exerts torque on the ring gear through the meshing teeth, the ring gear experiences a torque load. This torque load can be transmitted to other components or systems connected to the ring gear.
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio between the ring gear and the driving gear determines the speed and torque relationship between the two gears. The gear ratio is defined as the ratio of the number of teeth on the ring gear to the number of teeth on the driving gear. By changing the size or number of teeth on either the ring gear or the driving gear, the gear ratio can be adjusted to achieve the desired speed or torque output.
- Load Distribution: The ring gear distributes the load over a larger area compared to other types of gears. This load distribution characteristic allows the ring gear to handle higher loads and torque. The design of the ring gear and its tooth profile ensures that the load is evenly distributed across the surface of the gear, enhancing its durability and reducing the risk of premature wear or failure.
Ring gears are commonly used in various applications, including automotive transmissions, differential systems, planetary gear systems, industrial machinery, and power transmission equipment. They provide advantages such as compactness, high torque capacity, load distribution, and the ability to achieve high gear ratios.
It’s important to note that the design and characteristics of ring gears may vary depending on the specific application and requirements. Factors such as tooth profile, material selection, lubrication, and manufacturing techniques are carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and durability of the ring gear.


editor by CX 2024-04-11