Product Description
Slewing ring bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
Slewing ring bearing is a bearing that able to bear axial load, radial load and overturning torque. Under normal circumstances, slewing ring bearings have their own mounting holes, lubricant holes and seal holes, to meet the different needs of the various host working under the various conditions;
On the other hand, slewing ring bearing itself has characteristics of compact structure, guide rotating convenient, easy to install and maintaining easily.
2. Structure
2.1 Slewing ring bearings have different types as per different structures, here below is what we offering now:
Single row ball slewing ring bearings
Double row ball slewing ring bearings
Crossed roller slewing ring bearings
Three row roller slewing ring bearings
Flange slewing ring bearings
2.2 The above slewing ring bearings can also be divided into 3 different types as per different transmissions:
Slewing ring bearings with no gear
Slewing ring bearings with external gear
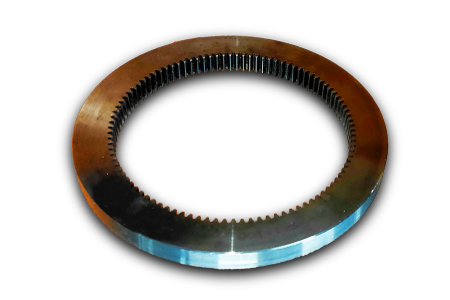
Slewing ring bearings with internal gear
3. Features:
Slewing ring bearings have more features: compact structure, reliable guide, simple installation, and easily maintenance
4. Application:
Slewing ring bearings can be widely used in lifting & transport machinery, mining machinery, construction machinery, port hoisting machinery, port oil transfer equipment, onshore and offshore crane, excavator, concrete machine, paper machine, plastic and rubber machine, weave machine, steel plant, electronic power plant, wind power generator, other construction and industry machines or equipments and other large rotary device
Single row ball slewing ring bearing:
1.Slewing bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing ring bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
The single row ball slewing ring bearing is composed of 2 seat-rings. The balls contact with the circular race at 4 points, via which the axial force, radial force and resultant moment may be born simultaneously.
2.2. Structure
Slewing ring bearings have different types as per different structures, here below is what we offering now:
Single row ball slewing bearing has 3 different types:
Single row ball slewing bearing with no gear
Single row ball slewing bearing with external gear
Single row ball slewing bearing with internal gear
Single row ball slewing ring bearing
1.Slewing bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing ring bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
The single row ball slewing ring bearing is composed of 2 seat-rings. The balls contact with the circular race at 4 points, via which the axial force, radial force and resultant moment may be born simultaneously.
2. Structure
Slewing ring bearings have different types as per different structures, here below is what we offering now:
Single row ball slewing bearing has 3 different types:
Single row ball slewing bearing with no gear
Single row ball slewing bearing with external gear
Single row ball slewing bearing with internal gear
3. Features
Single row ball slewing ring bearings have following features:
Compact in structure and light in weight.
4. Application:
Single row ball slewing ring bearings are widely used in slewing conveyers, welding arm and positioned, medium duty cranes, excavators and other engineering machines
Double row ball slewing ring bearing:
1.Slewing bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing ring bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
The double row ball slewing bearing has 3 seat-rings. The steel balls and the retainers may be directly arranged into the upper and lower racers. Two rows of steel balls with different diameters are fitted according to the force. Such open type fitting is extraordinary convenient, the loading angels at upper and lower races are 90°which can carry both of the axial force and capsizing moment. When the radial force is larger than 1/10 of the axial force, the races should be newly designed.
2. Structure:
Double row ball slewing bearing has 3 different types:
Double row ball slewing bearing with no gear
Double row ball slewing bearing with external gear
Double row ball slewing bearing with internal gear
3. Features:
Double row ball slewing ring bearings have following features:
Larger dimension of axial and radial and compact structure.
4. Application:
Double row ball slewing ring bearings are widely used in Tower cranes which require working radius over medium range, auto crane and loading (unloading) machinery.
Double row ball slewing ring bearing:
1.Slewing bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing ring bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
The double row ball slewing bearing has 3 seat-rings. The steel balls and the retainers may be directly arranged into the upper and lower racers. Two rows of steel balls with different diameters are fitted according to the force. Such open type fitting is extraordinary convenient, the loading angels at upper and lower races are 90°which can carry both of the axial force and capsizing moment. When the radial force is larger than 1/10 of the axial force, the races should be newly designed.
2. Structure:
Double row ball slewing bearing has 3 different types:
Double row ball slewing bearing with no gear
Double row ball slewing bearing with external gear
Double row ball slewing bearing with internal gear
3. Features:
Double row ball slewing ring bearings have following features:
Larger dimension of axial and radial and compact structure.
4. Application:
Double row ball slewing ring bearings are widely used in Tower cranes which require working radius over medium range, auto crane and loading (unloading) machinery.
Crossed roller slewing ring bearing
1.Slewing bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing ring bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
With the cross roller Ring, cylindrical rollers are arranged crosswise, with each roller perpendicular to the adjacent roller, in a 90° groove, separated from each other by a spacer retainer. This design allows just 1 bearing to receive loads in all directions including, radial, axial and moment loads. Since the Cross-Roller Ring achieves high rigidity despite the minimum possible dimensions of the inner and outer rings, it is optimal for applications such as joints and swiveling units of industrial robots, swiveling tables of machining centers, rotary units of manipulators, precision rotary tables, medical equipment, measuring instruments and IC manufacturing machines.
2. Structure:
Cross roller slewing bearing has 3 different types:
Cross roller ball slewing bearing with no gear
Cross roller ball slewing bearing with external gear
Cross roller ball slewing bearing with internal gear
3. Features
Cross roller slewing ring bearings have following features:
1. High precision: cross roller bearings can be made high precision bearings, at P4, P2.
2. High rigidity: These series roller bearings are with preload.
3. High load capacity: This series roller bearing can support axial load, radial load, and tilting load.
4. Small volume: this series roller bearing can save space for the machine.
4. Application
Cross roller slewing rings are widely applied in the precision rotary table, rotary joint of manipulator, medical equipment, and measuring instrument etc
Triple row roller slewing ring bearing
1.Slewing bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing ring bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
Three row roller slewing ring bearing has 3 seat-rings, which separate the upper, lower and radial raceway, via which the load of each row of the rollers may be specified. Thus it can carry different load simultaneously and its load capacity is the largest 1 of the 4 types
2. Structure:
Triple row roller slewing bearing has 3 different types:
Triple row roller slewing bearing with no gear
Triple row roller slewing bearing with external gear
Triple row roller slewing bearing with internal gear
3. Features
Triple row roller slewing ring bearings have following features:
Larger axial and radial dimension, compact structure
4. Application
Triple row roller slewing rings are widely used in heavy-duty machines which require large working radius, such as bucket-wheel excavators, wheeled cranes, ship cranes, ladle turret, auto cranes etc.
Flange Slewing Bearing
1.Slewing bearing is also called slewing ring, slewing ring bearing, turntable bearing, and rotary bearing.
Flange slewing bearing is a special slewing ring bearing, it can have 1 flange in the outer ring, or 1 flange in the inner ring, even it can have 1 flange in both inner ring and outer ring.
2. Structure:
Flange slewing bearing has 3 different types:
Flange slewing bearing with no gear
Flange slewing bearing with external gear
Flange slewing bearing with internal gear
3. Features
Flange slewing bearings have following features:
Compact structure and easily installment.
4. Application
Flange slewing bearings are widely used in tow truck, and other applications are the same as slewing bearings, such as lifting & transport machinery, mining machinery, construction machinery, excavator, concrete machine, paper machine, plastic and rubber machine and steel plant.
Excavator Slewing Bearing
Excavator slewing bearing is a special slewing ring bearing as per its applications. And it is a very important part for excavators, we can supply excavator slewing bearings for both second-hand excavators for maintenance and new excavators.
2. Structure:
Excavator slewing bearing are usually made as per single row ball slewing bearing structure, and most of them are internal gear types, but some are external gear types.
3. Features
Excavator slewing bearings have familiar features as single row ball slewing ring bearings.
Compact structure, light weight and easily installment.
4. Application
Excavator slewing bearings are widely used for all brands of excavators, such as Komatsu, Hitachi, Kobelco, Sumitomo, Doosan, Hyundai, Samsung, Caterpillar, Daewoo, Kato, Volvo, CHINAMFG and so on.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Standard or Nonstandard: | Standard |
|---|---|
| Feature: | High Speed, Vacuum, Antimagnetic, Cold-Resistant, Corrosion-Resistant, Heat-Resistant |
| Sealing Gland: | Sealed On Both Sides |
| Rolling-Element Number: | Single-Row |
| Roller Type: | Spherical Raceway |
| Material: | Bearing Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you choose the right size ring gear for your application?
Choosing the right size ring gear for a specific application involves considering several factors related to the gear system, load requirements, space constraints, and performance objectives. Here’s a detailed explanation of the process involved in selecting the appropriate size ring gear:
- Determine the Gear System Parameters: Understand the specific requirements of the gear system in which the ring gear will be used. This includes identifying the input power, desired output speed, torque requirements, and operating conditions such as temperature, vibration, and lubrication.
- Calculate Gear Ratios: Determine the required gear ratios for the gear system. Gear ratios define the relationship between the rotational speeds and torques of the driving and driven gears. By knowing the desired gear ratios, you can calculate the appropriate size of the ring gear relative to the other gears in the system.
- Evaluate Load Capacity: Assess the load capacity needed for the application. Consider the maximum torque and radial loads that the ring gear will experience during operation. It’s crucial to select a ring gear that can handle the anticipated loads without excessive wear, deformation, or failure.
- Consider Space Limitations: Determine the available space for the ring gear within the application. Consider the overall dimensions, such as the outer diameter, inner diameter, and thickness of the ring gear. Ensure that the selected size fits within the designated space without interfering with other components or compromising the overall functionality of the system.
- Account for Manufacturing Considerations: Consider the manufacturability of the ring gear. Evaluate factors such as the feasibility of producing the required tooth profile, the availability of suitable materials, and the manufacturing capabilities of the supplier. It’s important to choose a size that can be efficiently manufactured while meeting the required quality standards.
- Consult Design Guidelines and Standards: Refer to industry design guidelines, standards, and specifications specific to the type of gear and application. These guidelines provide recommendations and formulas for calculating gear sizes based on factors such as tooth strength, contact stress, and bending stress. Adhering to recognized standards ensures that the selected ring gear size is appropriate for the intended application.
It is often beneficial to consult with gear design engineers or industry experts to ensure the proper selection of the ring gear size. They can provide detailed analysis, simulation, and expertise in choosing the optimal size based on the specific requirements and constraints of the application.
By carefully considering these factors and following established design practices, you can choose the right size ring gear that will deliver reliable performance, efficient power transmission, and long-term durability for your application.
\
How do you maintain and service a ring gear system?
Maintaining and servicing a ring gear system is crucial to ensure its optimal performance, reliability, and longevity. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance and service procedures for a ring gear system:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the ring gear system to detect any signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or abnormal conditions. Inspect the gear teeth for chips, cracks, or excessive wear. Check for proper gear engagement and backlash. Inspect the mounting bolts or fasteners for tightness. Regular inspections help identify potential issues early on and prevent further damage or failures.
- Cleaning and Lubrication: Clean the ring gear system periodically to remove dirt, debris, and old lubricant. Use appropriate cleaning methods and solvents that are compatible with the gear system materials. After cleaning, apply fresh lubricant according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Ensure proper lubrication coverage and distribution to minimize friction, wear, and heat generation.
- Lubricant Analysis: Periodically analyze the condition of the lubricant in the ring gear system to assess its effectiveness and detect any contamination or degradation. Lubricant analysis involves collecting samples and sending them to a laboratory for testing. The analysis results can provide valuable information about the lubricant’s viscosity, contamination levels, and overall condition. Based on the analysis, determine whether lubricant replacement or additional maintenance actions are necessary.
- Bearing and Seal Inspection: If the ring gear system includes bearings or seals, inspect them regularly for wear, damage, or leaks. Check for excessive play, noise, or overheating in the bearings. Inspect the seals for proper sealing and lubricant retention. Replace any worn-out bearings or damaged seals to prevent further damage to the ring gear system.
- Torque Checks: Periodically check the torque of the mounting bolts or fasteners that secure the ring gear system. Over time, vibrations and operational stresses can cause bolts to loosen. Ensure that the bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Perform torque checks during scheduled maintenance intervals or when any signs of loosening are observed.
- Alignment and Gear Meshing: Check and adjust the alignment of the ring gear system if necessary. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear, increased load on the gear teeth, and reduced performance. Ensure proper gear meshing and backlash according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Adjust the gear positioning or contact pattern if deemed necessary during inspections or maintenance activities.
- Repair or Replacement: If any significant damage, wear, or malfunction is identified during inspections or maintenance activities, plan for repair or replacement of the affected components. Depending on the severity and nature of the issue, repairs may involve repairing gear teeth, replacing damaged parts, or realigning the gear system. If extensive damage is present or the gear system has reached the end of its service life, consider replacing the entire ring gear system.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed documentation and records of all maintenance and service activities performed on the ring gear system. Keep track of inspection results, lubrication schedules, repairs, parts replacements, and any other relevant information. These records help establish a maintenance history, track performance trends, and provide valuable reference information for future maintenance and troubleshooting.
It’s important to note that the specific maintenance and service procedures may vary depending on the type of ring gear system, its application, and the manufacturer’s guidelines. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and consult with experts or professionals when necessary to ensure proper maintenance and servicing of the ring gear system.
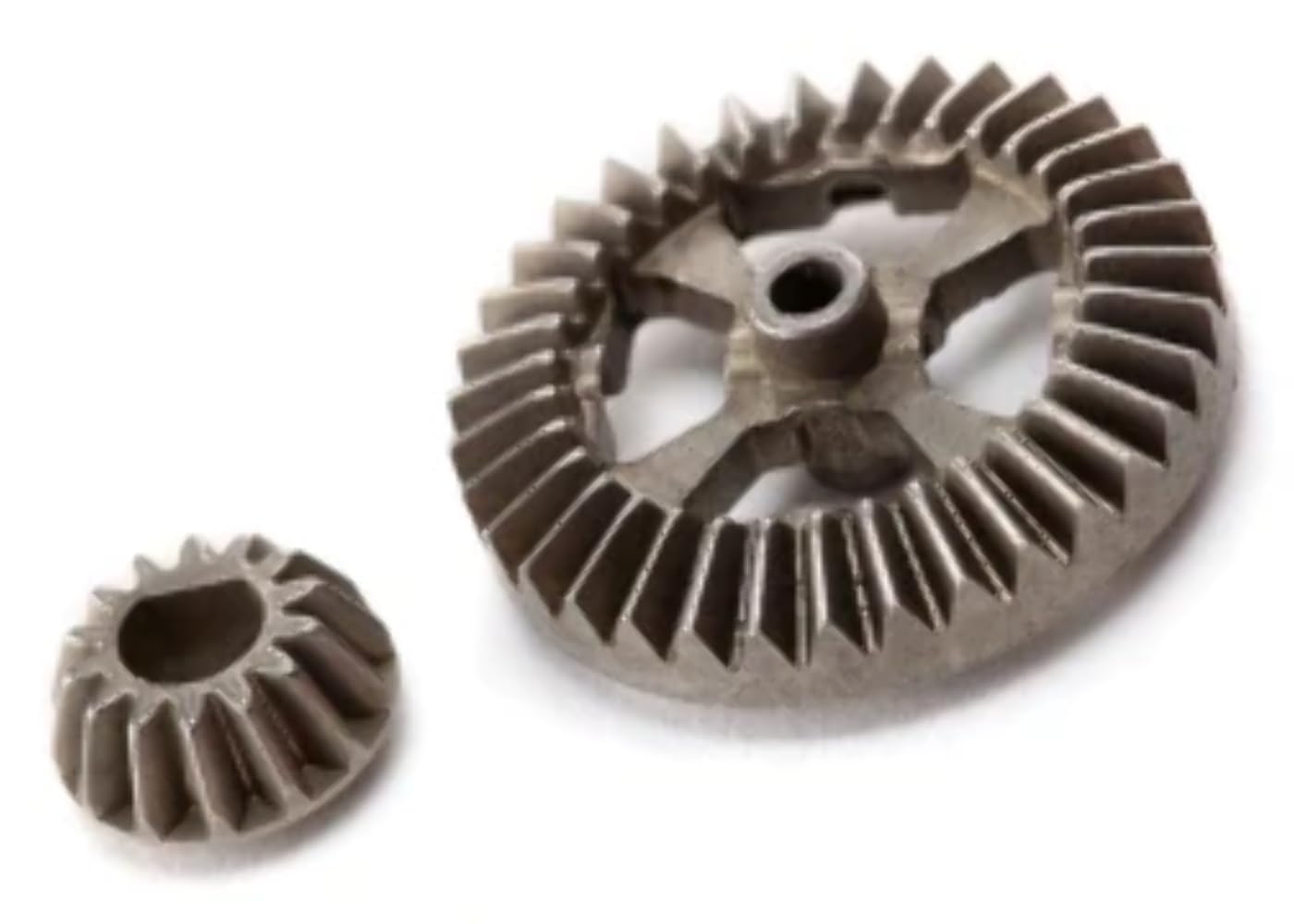

What is a ring gear and how does it work?
A ring gear is a type of gear that features teeth on the outer perimeter of a circular ring-shaped component. It is commonly used in various mechanical systems and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of what a ring gear is and how it works:
A ring gear, also known as an annular gear or internal gear, is a gear with teeth on the inside circumference of a circular ring. It is designed to mesh with a pinion gear or another gear that has teeth on the outside. The combination of a ring gear and a pinion gear forms a gear set, enabling the transmission of rotational motion and torque between the two gears.
Here’s how a ring gear works:
- Tooth Engagement: When a ring gear and a pinion gear are brought together, the teeth of the pinion gear mesh with the teeth of the ring gear. The teeth of the pinion gear enter the spaces between the teeth of the ring gear, creating a mechanical connection between the two gears.
- Motion Transmission: As the driving gear (such as the pinion gear) rotates, it transfers rotational motion to the ring gear. The teeth of the driving gear push against the teeth of the ring gear, causing the ring gear to rotate in the opposite direction. This rotational motion can be used to drive other components or systems connected to the ring gear.
- Torque Transfer: The meshing of the teeth between the ring gear and the driving gear allows for the transfer of torque. Torque is the rotational force or twisting force applied to a gear. As the driving gear exerts torque on the ring gear through the meshing teeth, the ring gear experiences a torque load. This torque load can be transmitted to other components or systems connected to the ring gear.
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio between the ring gear and the driving gear determines the speed and torque relationship between the two gears. The gear ratio is defined as the ratio of the number of teeth on the ring gear to the number of teeth on the driving gear. By changing the size or number of teeth on either the ring gear or the driving gear, the gear ratio can be adjusted to achieve the desired speed or torque output.
- Load Distribution: The ring gear distributes the load over a larger area compared to other types of gears. This load distribution characteristic allows the ring gear to handle higher loads and torque. The design of the ring gear and its tooth profile ensures that the load is evenly distributed across the surface of the gear, enhancing its durability and reducing the risk of premature wear or failure.
Ring gears are commonly used in various applications, including automotive transmissions, differential systems, planetary gear systems, industrial machinery, and power transmission equipment. They provide advantages such as compactness, high torque capacity, load distribution, and the ability to achieve high gear ratios.
It’s important to note that the design and characteristics of ring gears may vary depending on the specific application and requirements. Factors such as tooth profile, material selection, lubrication, and manufacturing techniques are carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and durability of the ring gear.


editor by Dream 2024-04-30